- 中
- +86 13732210605
Author:Haze Meter
Haze Meter, I believe many people may think at first sight that it is an instrument for measuring weather haze and operating like a thermometer! Of course not! Today's popular science is optical instrument Hazemeter, which belongs to precision instrument, as shown in the figure below:

Unlike the customized single function of mercury thermometer to measure human body temperature, the haze meter is not only more powerful, but also different models. For example, the color spectrum haze meter is mainly used for haze detection, total transmittance detection and spectral transmission performance detection of transparent and translucent parallel plane materials such as plastic, film, glass products and LCD panel. In addition to a wide range of applications, it can measure haze, transmittance and other parameters. Some haze meters can also detect color difference!
Having finished the general concept of the haze meter, let's take a look at the real face of the haze meter!
To understand the haze meter, we must first know two concepts: haze and transmittance
Haze is also called turbidity Indicates the degree of opacity of transparent or translucent materials It refers to the appearance of cloud or turbidity caused by light scattering inside or on the surface of a material Expressed as a percentage of the ratio of the scattered luminous flux to the luminous flux through the material. Generally, only the scattered luminous flux that deviates from the direction of incident light by more than 2.5 degrees is used to calculate haze. The distance produces beauty, and the haze is the same. The haze and display effect of the same piece of glass are different, as shown in the figure:

Calculation principle of haze
A beam of parallel light from the standard "C" light source is vertically irradiated on the transparent or translucent film, sheet and plate. Due to the scattering caused by the interior and surface of the material, all the light passing through the object makes part of the parallel light deviate from the incident direction by more than 2.5 °, which is the percentage of the ratio of the scattered luminous flux td to the luminous flux T2 passing through the material, that is:
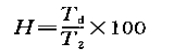
Calculation principle of transmittance
Transmittance, expressed as a percentage of the ratio of the luminous flux through the material to the incident luminous flux. It usually refers to the ratio of the luminous flux T2 through the material to the incident luminous flux T1 irradiated on the transparent material by a beam of parallel light of the standard light source, that is:

If the light passing through the glass is compared to the soldiers breaking through the customs, the first thousand troops and horses are called the incident luminous flux T1, which cuts through thorns and thorns all the way, with some casualties, and the rest are called T2. Among the soldiers entering the pass, in addition to those who continue to move forward with the army, some may escape to all parties affected by the battle. We call the deserter who deviates from the driving direction of the army by 2.5 ° TD.
What is the relationship between the two?
Haze and transmittance are two very important optical performance indexes of transparent materials. In packaging applications, hazy films may reduce the quality feeling of consumers, such as the appearance of packaging products. Generally speaking, the haze value of materials with high light transmittance is low, and vice versa, but not completely. Some materials have high light transmittance but high haze value, such as ground glass. Therefore, transmittance and haze are two independent indicators.

After reading the above introduction, do you have a preliminary understanding of the haze meter? If you have any questions, please leave a message and consult our company!

